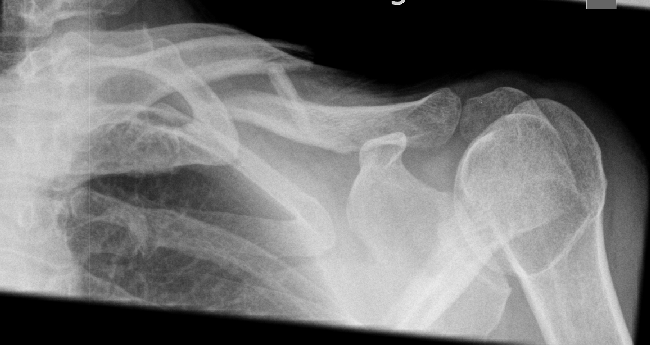
Clavicle Fracture
Clavicle fractures commonly occur following a fall onto the outer aspect of the shoulder eg rugby, falling from bike. In some cases, the fracture can be treated with a sling and a reasonably good outcome can be obtained. However, some clavicle fractures do not heal correctly with non surgical treatment and can lead to long term problems which can be quite disabling. Malunion means that the fracture unites in the wrong position resulting in permanent shortening of the clavicle with associated deformity.
Deciding which clavicle fracture can be treated non-operatively and which one requires surgery is the key to management. Generally speaking, the indications for early surgical fixation are:
- Fractures with overlap or displacement greater than 2 centimeter, this will otherwise result in significant shortening
- Displaced fracture with tenting of the skin, there is a high chance of non union
- Scapula fracture on the same side, this combination is sometimes referred to as floating shoulder
- Comminuted fracture caused usually by high velocity trauma
- Multiple fractures associated scapula fracture ( floating shoulder )
- Open (compound) fracture
- Associated nerve or blood vessel injury
- The above are particularly important for a professional sports person
The advantages of early fixation of clavicle fracture include:
- Earlier return to work and physical activities
- Less pain as the fracture has now been stabilised
- Restoration of length of clavicle and prevention of malunion and associated step deformity
- Less chance of non union and fibrous union since the two ends of the fracture are now anatomically aligned
The disadvantages of surgery include:
- Risk of infection
- Scar
- There can sometimes be patchy area of numbness around the scar which usually settles and improves with time
- Possible need for a second operation to remove the underlying plate and screws once the fracture has united
- Risk of non union
There is more and more evidence now that early clavicle fracture fixation is associated with a far better outcome than non-operative management.
Further ReadingNonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. Altamimi SA, McKee MD. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Mar;90 Suppl 2 Pt 1:1-8
‘Operative fixation of a displaced fracture of the clavicular shaft results in improved functional outcome and a lower rate of malunion and nonunion compared with nonoperative treatment at one year of follow-up. This study supports primary plate fixation of completely displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in active adult patients.’